Introduction to Medical Oncology
Biologic Therapies


Portfolio


Did You Know...
Biologic Therapies
The immunomodularity and pro-apoptotic effects of some cytokines (interferons, interleukins) can be exploited therapeutically in some maliganacies, for example: malignant melanoma, renal cell carcinoma and chronic myeloid leukemia.
Review Questions
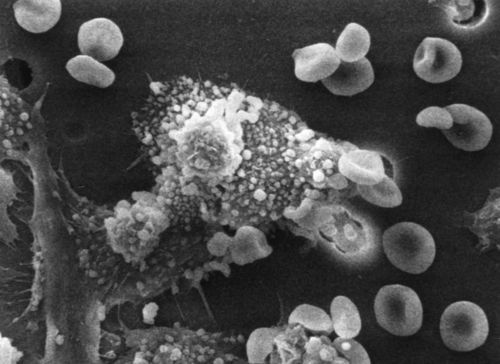
the death of a cancer cell
Dr. Raowf Guirguis. National Cancer Institute, Susan Arnold (photographer), October 1988
 Previous
Previous